Description:
Overview
Over many years, Silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafers are offering a great benefit over traditional silicon device structure due to their improved electrical isolation, reduced parasitic capacitances, improved radiation hardness, and higher packing density [1]. But at the same time, the buried oxide in SOI metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) structures electrically and thermally insulates the active channel from the substrate. As a result, the temperature can rise excessively in SOI MOSFETs leading to performance degradation and early thermal breakdowns. Therefore, effective thermal management becomes a vital part here to ensure the long term reliability and optimal performance.
Input Data
The model can be made using the dimensions as shown:
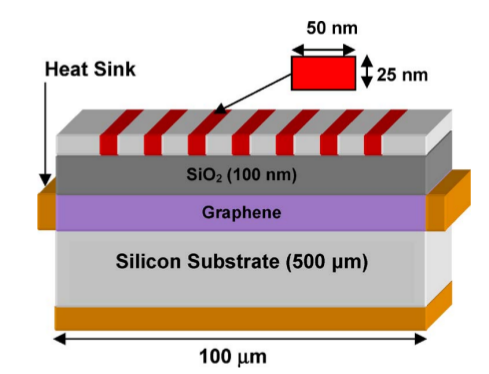
Geometry dimensions from [1]
The material data for each component can also be extracted from [1].
Purpose
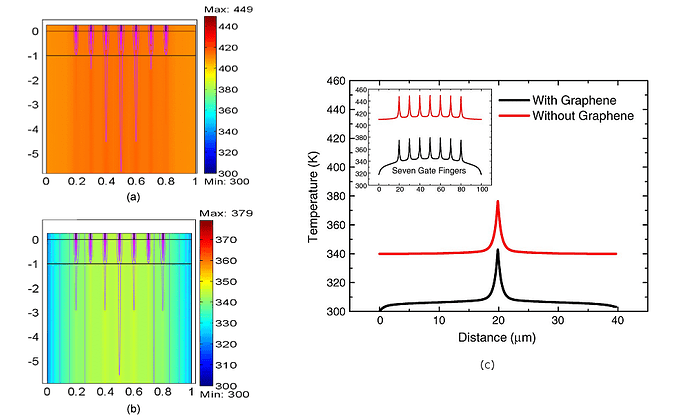
The purpose of this project is to study the feasibility of a graphene as a lateral heat spreaders in SOI-based chips. The effectiveness of the heat removal via graphene material from these type of chips is the main goal here. The results for comparison can be found below:
Temperature distribution across SOI with seven active transistors (a) without graphene and (b) with graphene heat spreaders attached to heat sinks. (c) Temperature profile over the top surface of SOI MOSFET with and without graphene heat spreaders [1].
Key Words
Graphene, heat conduction, heat spreaders, hot spots, silicon-on-insulator (SOI), thermal management.
Literature & Sources
- [1] Subrina, Samia, Dmitri Kotchetkov, and Alexander A. Balandin. “Heat removal in silicon-on-insulator integrated circuits with graphene lateral heat spreaders.” IEEE Electron Device Letters 30.12 (2009): 1281-1283.
Status
Not yet started.