Question
Nonlinear and dynamic analysis by default use a relative residual as a measure of convergence in their solution methods. In special cases this is not appropriate and an absolute residual should be used.
What is the difference between relative and absolute residuals and when is an absolute residual required?
Solution
A relative residual is defined as,
Immediately we can see that a problem arises if the external forces equal 0 at any point during the simulation. A math error occurs and the simulation will crash. This means that for simulations in which no external force is present for a given period an absolute residual must be applied where,
There are many physical applications in which no external force would be present for a period of the simulation. Typical examples include:
- Loading-unloading situations in which force is applied and then removed
- Objects colliding from a distance
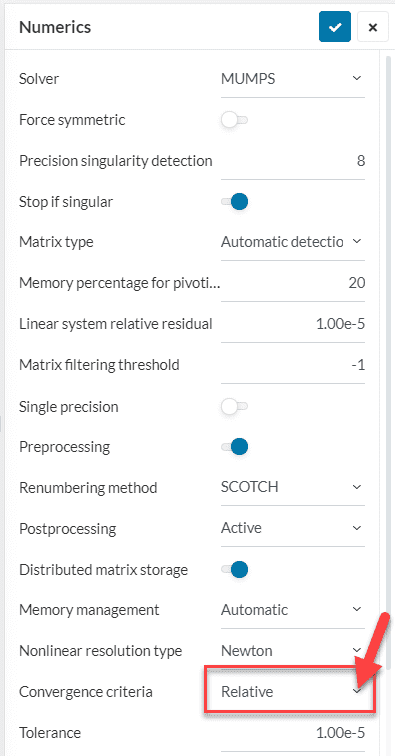
Switching between absolute and relative residual definition is achieved under the ‘Numerics’ dialog as shown below,
Important Information
If none of the above suggestions did solve your problem, then please post the issue on our forum or contact us.