Error
Memory allocation error. In order to prevent this error, please choose a machine with more computing cores and use less cores for the computation. Another option would be to change the linear system solver to an iterative solver like PETSC.
Error
An error appeared while allocating memory. If you are using the Multfront or LDLDT solver, please choose a larger machine by increasing the number of computing cores. For the MUMPS and PETSC solvers you should additionally reduce the number of parallel processes used for the computation to allow a higher RAM per CPU ratio.
What Happened?
The solver failed while allocating memory during the simulation run.
What Could Be the Possible Reason?
This error occurs when there are insufficient memory resources for the generated mesh.
What Can I Do Now?
Follow the steps below to resolve this error:
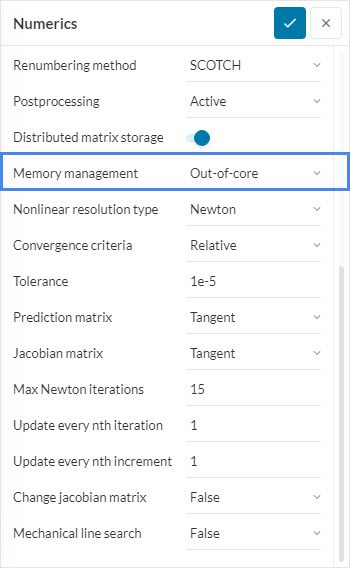
- Use the out-of-core memory functionality: If you are using the ‘MUMPS’ solver, activate the ‘Out-of-core’ function for Memory management in the Numerics settings. This enables memory management optimized for minimal RAM usage. However, the computation speed will be reduced since a portion of the data is written to the hard disk.
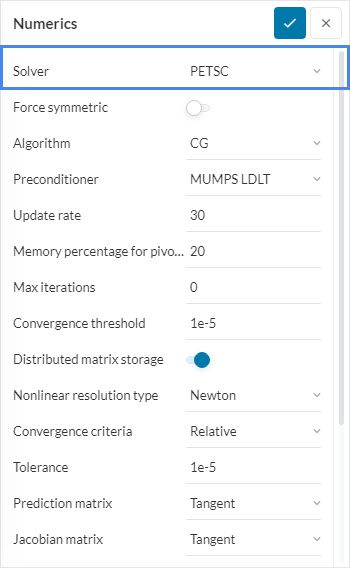
- Change the equation solver: If you are using a direct solver such as ‘MultFront’, ‘MUMPS’ or ‘LDLT’, try changing to an iterative solver like ‘PETSC’ under Numerics. Iterative solvers generally use less memory than direct solvers but may cause instability.
Note
The following steps are applicable only to Professional Users since it involves increasing the number of cores or decreasing the number of parallel processes.
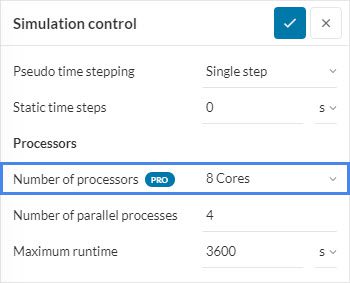
- Increase the number of cores: Machines with more cores will generally have more memory resources available. This can be done by going to Simulation control in your workbench and choosing a larger Number of processors. For example, for a mesh with more than a million nodes, assign at least ‘8’ cores.
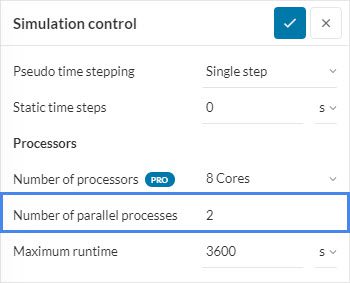
- Increase the RAM-per-CPU ratio: If the solver you are using is ‘MUMPS’ or ‘PETSC’, reduce the Number of parallel processes under Simulation control. This is because these linear solvers are parallelized in a way where the memory consumption does not depend on the total available memory of the machine, but instead on the available memory per computing core. Therefore, during memory allocation, more memory will be available for each CPU.
Important Information
If none of the above suggestions solved your problem, then please post the issue on our forum or contact us.