Documentation
This validation case belongs to solid mechanics. This test case aims to validate the following parameters:
The simulation results of SimScale were compared to the results derived from [Roark]\(^1\).
The geometry used for the case is as follows:
The beam has a length \(L\) of 1 \(m\), with the cross-section dimensions as shown:
| Parameter | Value [\(m\)] |
|---|---|
| B | 0.06 |
| H | 0.08 |
| b | 0.04 |
| h | 0.06 |
Tool Type: Code_Aster
Analysis Type: Static Linear
Mesh and Element Types:
Tetrahedral meshes were computed using SimScale Standard mesh algorithm and manual sizing. The table below shows an overview of the mesh characteristics.
| Case | Mesh Type | Number of Nodes | Element Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Standard | 3345 | 1st order tetrahedral |
| B | Standard | 20742 | 2nd order tetrahedral |
Material:
Boundary Conditions:
The analytical solutions for the deflection \(w\) at the free end of the beam are given by the following equations. The remote force \(F\) is substituted with a force and moment pair \(M\):
$${M = Fd} \tag{1}$$
$$ w = \frac{F L^3}{3 E I} + \frac{M L^2}{2 E I} \tag{2} $$
$$ I = \frac{1}{12} ( B H^3 – b h^3) \tag{3} $$
The computed reference solution is:
$$ M = 1000\ Nm $$
$$ I = 1.84×10^{-6}\ m^4 $$
$$ w = 2.209×10^{-3}\ m $$
Comparison of displacement DZ of the center point of face B with the computed reference solution \(w\):
| CASE | DZ [\(10^{-3}\ m\)] | \(w\) [\(10^{-3}\ m\)] | Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.14109 | 2.209 | 3.07 % |
| B | 2.2121 | 2.209 | -0.14 % |
Comparison of the neutral fiber deflection shapes:
And finally, a plot showing the deformed shape and the magnitude of DZ displacement:
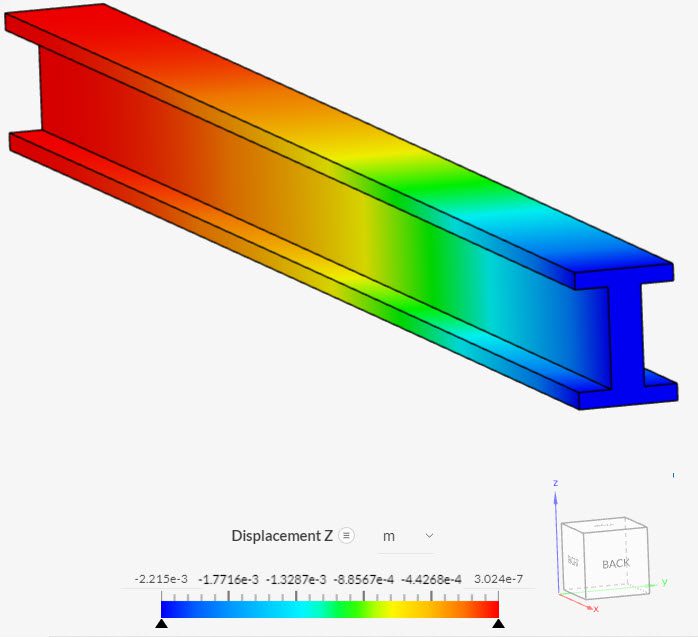
References
Note
If you still encounter problems validating your simulation, then please post the issue on our forum or contact us.
Last updated: September 9th, 2022
We appreciate and value your feedback.
Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now