Documentation
Young’s modulus or elastic modulus is a mechanical property of linear elastic solid materials. It defines the relationship between stress and strain in a solid material, and is given by:
$$ \sigma = E \varepsilon $$
where,
Young’s modulus has units of pressure or stress (\(Pa, psi \)) since the strain is a dimensionless quantity. From the given relation, it can be seen that the elastic modulus is the ratio between stress and strain:
$$ E = \frac{ \sigma }{ \varepsilon } $$
Physically speaking, it is a measure of how rigid a material is. As the overall rigidity of a part is also dependent on the geometrical shape, it is necessary to have a shape-independent property to measure the material.
A solid material is called elastic if it can naturally return to its original shape after the applied loads are removed. On the other hand, if the ratio between stress and strain is constant during the deformation process, then Young’s modulus is also a constant, and the material is considered to be linear elastic.
The material properties can be defined via isotropic or orthotropic properties.
Learn more about linear elastic materials in the following document:
In general, all solid materials are not linear elastic, especially when they are subjected to high levels of deformation. Figure 2 shows an example stress-strain curve for a ductile carbon steel material, as obtained from a uniaxial tension test:
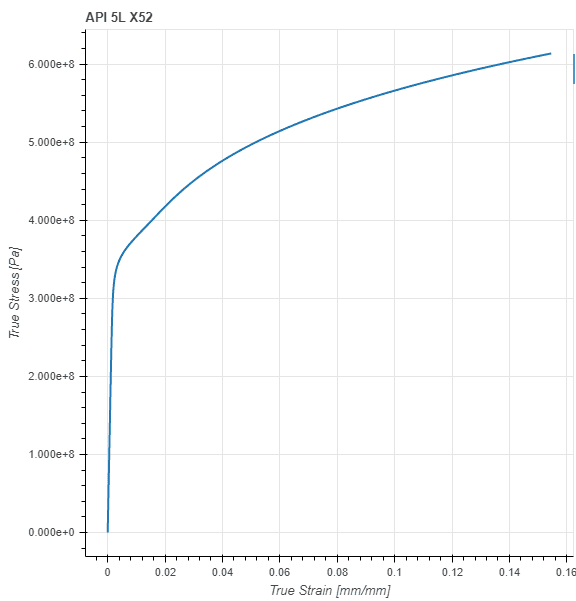
It can be seen that the material has a linear elastic behavior only for small strain values. When deformation increases, nonlinear behavior starts to occur. In this case, the ductile material exhibits plasticity, but other nonlinearities such as hyperelasticity or fragile rupture can also occur.
In general, most materials can be approximated to be linear elastic under the assumption of small deformation. In that case, the elastic modulus can be approximated by analyzing the linear portion of the stress-strain curve, and computing:
$$ E_y = \frac{ \sigma_y }{ \epsilon_y } $$
where,
When setting up a structural simulation, Young’s modulus parameter for an elasto-plastic material is specified as follows:
Learn more about elasto-plastic materials in the following document:
Linear Elastic vs. Elasto-plastic
In conclusion we can say for:
Last updated: May 23rd, 2025
We appreciate and value your feedback.
Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now