Documentation
Boundary conditions define how a system -( for example, a structure or a fluid )- interacts with the environment. Fixations, loads, pressures, flow rates, or velocities are all examples of boundary conditions.
A boundary condition consists of three pieces of information:
SimScale offers many boundary condition types for different types of applications. Boundary conditions are only displayed when they can be applied to the type of analysis being worked on. The following list shows the available boundary condition types, what each type means, and where they can be used. For advanced users, the page also shows how the boundary condition types translate to the solver input files.
To create a new boundary condition, click on the ‘+ button‘ next to Boundary conditions. Pick the desired one from the list:
After creating a boundary condition, assign the desired entities by clicking on them.
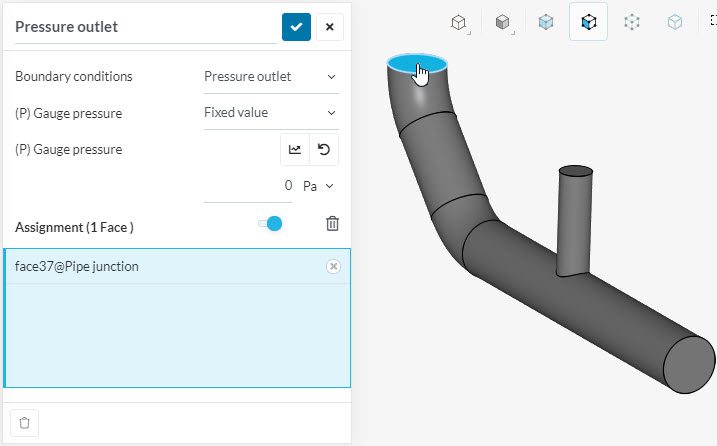
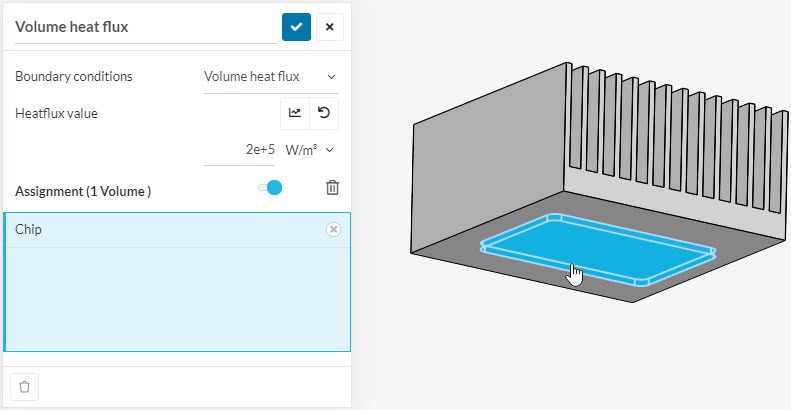
All of the fluid dynamics boundary conditions are assigned to faces exclusively. For solid mechanics and thermodynamics, some boundary conditions only be assigned to volumes, such as Volume heat flux.
Lastly, some of the solid mechanics boundary conditions accept assignments of both faces and volumes, such as the Rotating motion boundary condition.
For simple cases, boundary conditions are defined by a single value of a given variable (velocity, temperature, pressure…). For advanced cases where a fixed value is not enough, alternative techniques are available:
Last updated: August 16th, 2024
We appreciate and value your feedback.
Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now