Documentation
The Incompressible fluid flow analysis is used to run fluid simulations where density variations are negligible. This assumption is typically valid when velocities and temperature gradients are small.
Mathematically speaking, the divergence of the flow velocity (\(u\)) is zero:
$$\nabla.u = 0$$
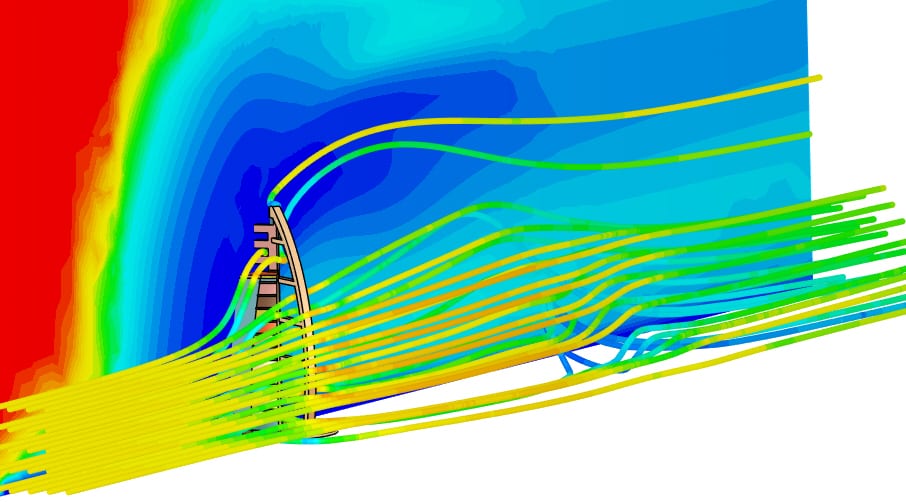
Within SimScale, one can effortlessly set up an incompressible simulation with the steps described below.
To create an incompressible analysis, first, select the desired geometry and click on ‘Create Simulation’:
Next, a window with a list of several analysis types supported in SimScale will be displayed:
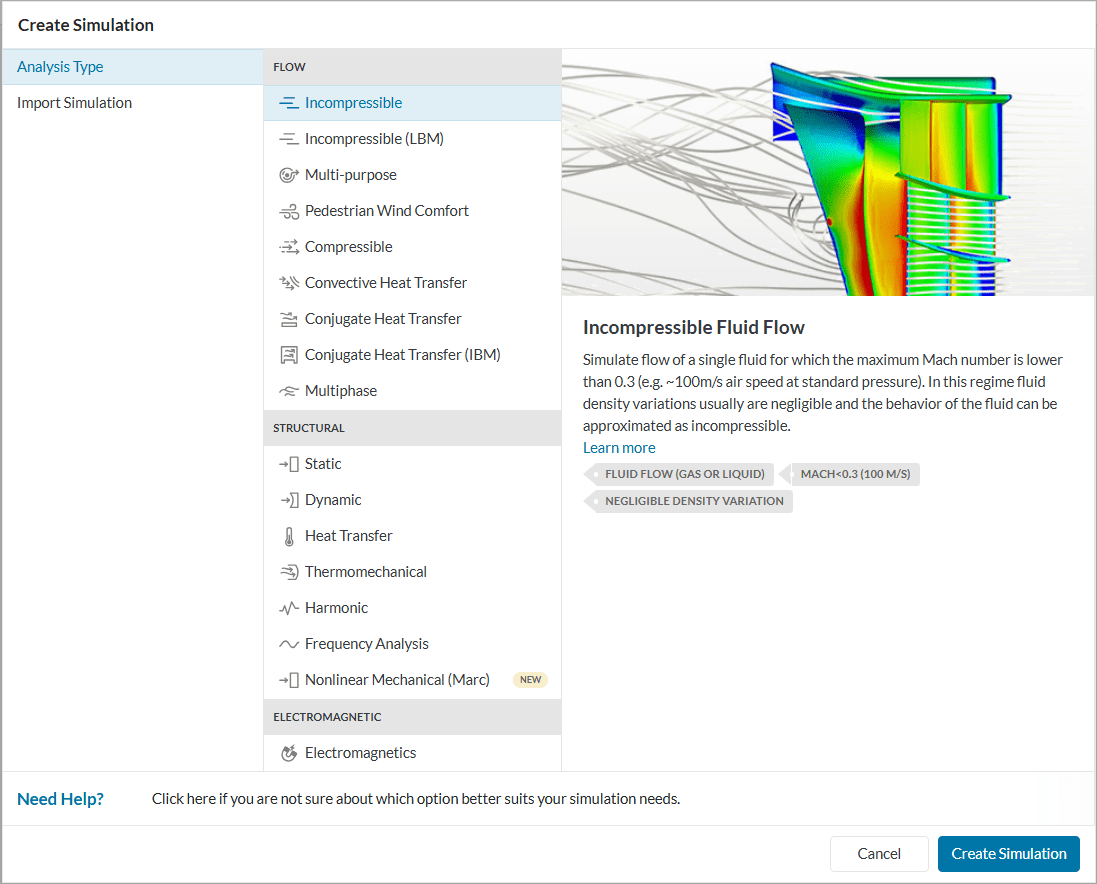
Choose the ‘Incompressible’ analysis type and click on ‘Create Simulation’. This will lead to the workbench for the incompressible flow simulation with the following simulation tree and the respective settings:
To access the global settings, click on ‘Incompressible‘ in the simulation tree. It consists of certain parameters that can be selected to define the fluid simulation. The parameters are listed below:
For detailed information about each of these parameters, visit the global settings page.
The Geometry section allows you to view and select the CAD model required for the simulation. It is important that the CAD model is well prepared to avoid any meshing or simulation related errors. Find more details on CAD preparation and upload here.
This section only appears if an LES (large eddy simulation) turbulence model is chosen inside global settings. Here, parameters related to the delta coefficient in LES need to be specified.
Find further information about the model section here.
Here, the appropriate fluid for the simulation can be specified. The user has the freedom to select the fluid properties based on the chosen Viscosity model. For more information, please visit the relevant documentation page for materials.
In an incompressible simulation, the computational domain will be solved for two fields: pressure \((P)\) and velocity \((U)\). Additional turbulent transport quantities may be included based on the turbulence model selected. Under Initial conditions, these values can be initialized for the whole domain or a sub-domain.
Important
For any simulation, initial and boundary conditions must be specified for all required variables on every boundary.
It is recommended to set the initial conditions close to the expected solution to avoid potential convergence problems. Alternatively, SimScale provides the possibility to use a potential flow solver to initialize the field before starting the actual simulation. This option is available under Simulation Control.
Learn how the initialization process takes place in depth in this document.
Boundary conditions help to add closure to the problem in hand by defining how a system interacts with the environment. Check out this detailed list of available boundary conditions and how they can be applied to the domain boundaries.
Some boundary conditions available in incompressible simulations are supported in parametric experiments. Learn more details in this article.
Important
In case no boundary conditions are assigned to a face, by default it will receive a no-slip wall boundary condition with wall function for turbulence resolution.
Under Advanced concepts, you will find additional setup options, such as Rotating zones, Momentum sources, Porous media, Solid body motions, and Passive scalar sources. Visit this dedicated page for more information.
Furthermore, momentum sources and rotating zones are supported in parametric experiments. Please visit this article for more details.
Numerical settings play an important role in the simulation configuration. They define how to solve the equations by applying proper discretization schemes and solvers to the equations. They help enhance the stability and robustness of the simulation. Although all numerical settings are made available for users to have full control over, it is advised to keep them default unless necessary.
Note
SimScale uses its own version of OpenFOAM® solvers developed in-house.
Numerical settings are recommended for advanced users but interested readers are encouraged to learn more about them through this documentation.
The Simulation control settings define the general controls over the simulation. In this tab, a series of variables can be set. For example, the End time and Maximum runtime for the simulation can be defined.
For a complete overview of the parameters and their meaning, check this page.
The Result Control section allows users to define additional simulation result outputs. It controls how the results will be written meaning the write frequency, location, statistics of the output data, etc.
Find more details about result controls here.
Meshing is the process of discretization of the simulation domain. That means we split up a large domain into multiple smaller domains and solve equations for them.
For an incompressible analysis, the standard, hex-dominant, and hex-dominant parametric algorithms are available. To learn more about the mesh settings in SimScale and its upload, visit this page.
SimScale offers a large number of tutorials on incompressible fluid flow each with a different purpose. Interested? Quickly check out our page for all the basic and advanced tutorials.
Last updated: July 17th, 2025
We appreciate and value your feedback.
Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now