Thermal bridging has a significant impact on the thermal and energy performance of buildings and structures. Heat (and hence, energy) is conducted through solid elements of a buildings’ structure and is lost through the envelope. This is often unaccounted for in the original energy and thermal design calculations because it is difficult to predict and manage. Overall, the energy lost through thermal bridges makes the design less energy-efficient and can lead to compliance failure with building regulations and standards.
SimScale allows architects and engineers to model the impact of heat conduction and thermal bridging on their building designs using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation in the cloud. WithSimScale, designers can benefit from more accurate thermal bridging predictions, as well as the ability to visualize heat conduction inside and outside of building models.
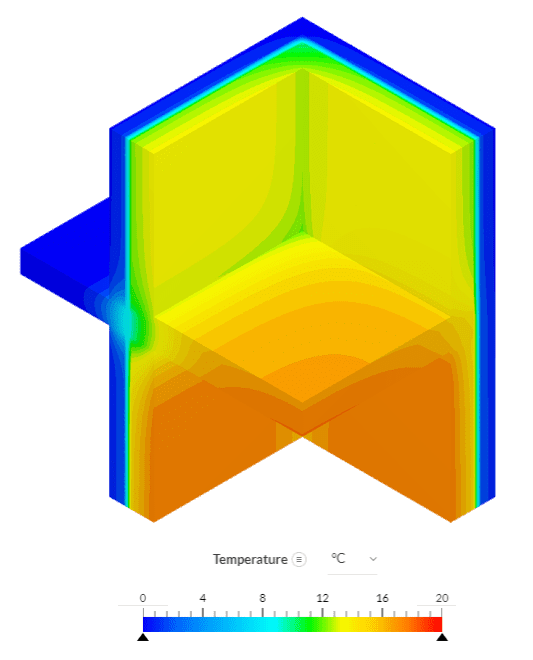
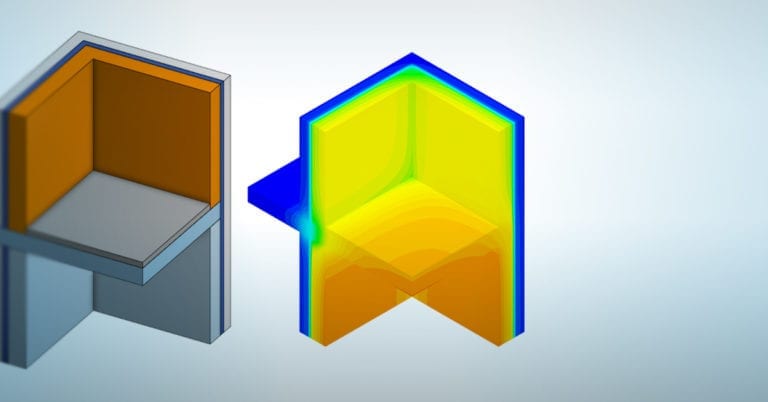
An example can be seen in the image below which shows a heat transfer analysis on two walls meeting at a corner, and a floor element—perhaps one of the most common applications for thermal bridging calculations.
The heat transfer analysis is performed to compare the temperature distributions and the heat flux between the internal and external environment and the acceptance criteria is based on ISO 10211:2007. The difference between the predicted temperatures using CFD and by the method being validated and the temperatures listed in the standard should not exceed 0.1 °C.
SimScale shows a temperature difference of 0.026 °C, well within the acceptable range.
Download the recording of our 30-minute demonstration to learn how to perform thermal bridging and heat conduction simulations in SimScale.
To learn more about the features and benefits of cloud-based CFD simulation for architecture and construction professionals, explore our additional resources below:
- The Building Design Process: Simulation at Every Step
- Digital Innovations in the Design of Sustainable Buildings
- Evaluating Design With BIM Modeling and Simulation