Traditional CAD and CAE tools constrain design space exploration with closed ecosystems and environments, limited hardware, and licensing costs. Performing a design space and performance optimization with these desktop-centric tools comes with significant barriers to entry that prevents design studies from taking place across many applications. By leveraging the power of end-to-end shape optimization completely in the cloud, the cost of expensive hardware and software maintenance fees are eliminated. And, with the advances in cloud CAD, CAE, and design optimization software, the workflows can be seamlessly integrated.
Case Study: Optimizing Design for Improved Performance
In this project, SimScale, Onshape, and Datadvance collaborated to optimize the geometry of an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) cooling plate design. The objective of this study was to minimize the average surface temperature for maximum thermodynamic efficiency while also minimizing the pressure drop or drag power on the cooling fluid in order to increase the fluid dynamic efficiency of the cooling plate. The project serves as a model for how shape optimization can be used in conjunction with thermo-fluid dynamics to optimize the design.
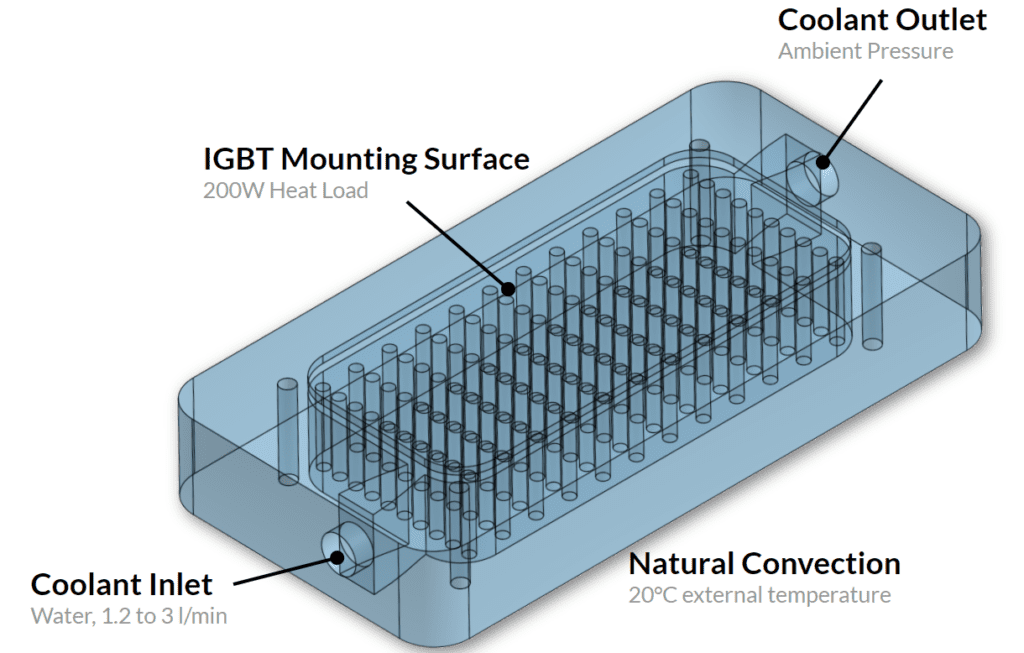
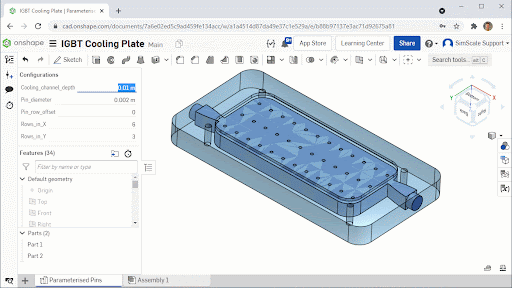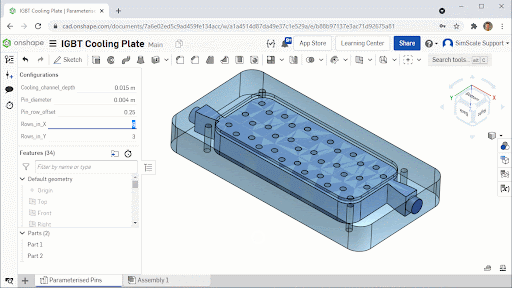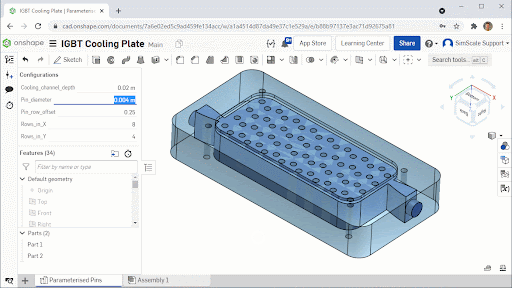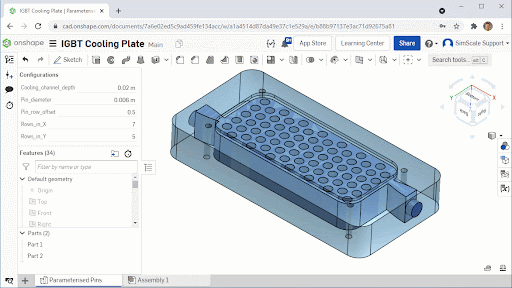
The cooling plate consists of a milled aluminum block with vertical pins to increase the surface area between the cooling fluid and the IGBT hot surface. The geometric variables were selected to ensure that any final design could be manufactured using approximately the same tooling and manufacturing methods:
- Pin diameter: 2 mm – 6 mm
- Pin row offset: 0 – 0.5 row width
- Pin rows in X: 6, 7 or 8
- Pin rows in Y: 3, 4 or 5
The flow rate was varied in an achievable range for the cooling pump:
- Flow rate: 1.2 l/min – 3 l/min
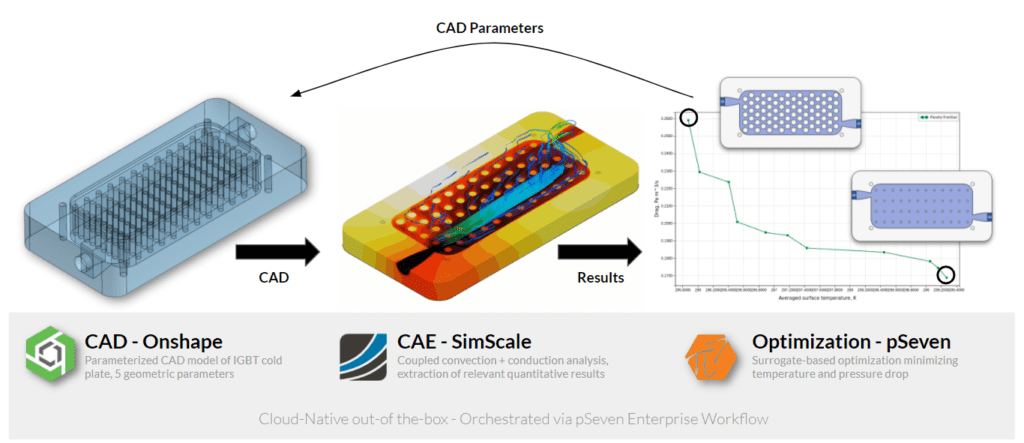
The IGBT geometry was modeled in Onshape and the geometric variables were parameterized so that they could be driven by pSeven, Datadvance’s optimization software through the Onshape Python Application Programming Interface (API).
If a single design is investigated, the workflow begins by generating the geometry in Onshape, with a specified parameter set. For that specific design, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation is conducted in the cloud using SimScale. As relevant quantitative results are extracted from the SimScale simulation, the next step is to set up a surrogate-based optimization in pSeven. The parameters which need to be altered to minimize temperature and pressure drop, hence optimizing the design, can be intelligently decided. Instead of following this procedure one by one for each parameter variation, a feedback loop for the CAD parameters between the optimized design obtained from pSeven and Onshape within this project was established. The API was used to automate the parameter variation and provide programmatic access to preprocessing, simulating, and postprocessing.
Cloud-Native Design Space Exploration
API gives analysts the ability to automate the workflows, explore parameter spaces automatically, and optimize the shape by connecting to the CAD authoring and optimization tools. Within this parameterization study, the API connected the geometric optimization tool to Onshape’s cloud-based design tool and to SimScale’s cloud-native multiphysics simulation engine. pSeven Enterprise was used to build and run the optimization workflow. Each time a particular geometry and simulation parameters were sent to the API, SimScale simulated the model and returned outputs for that instance, including temperature distribution, pressure, and efficiency. Data was then fed into the pSeven surrogate optimization model. As the workflow is scalable, many hundreds of geometric scenarios can be modeled. The physics outputs for each scenario were tracked using a Pareto front to converge on the local minima (the optimized solution) where the average surface temperature and the pressure drop were the key parameters.
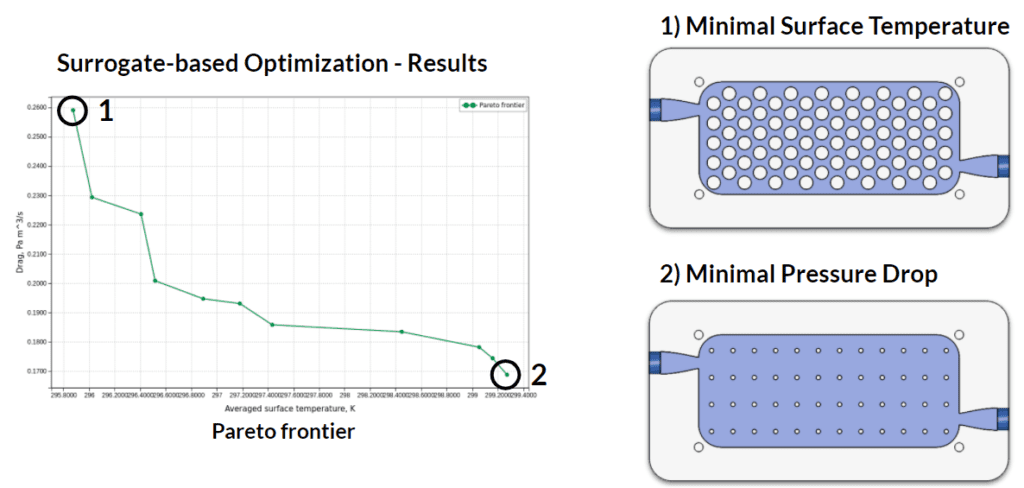
The results of the workflow showed that the highest pin density, with pin offset, gave the minimum surface temperature. However, the minimum pressure drop was obtained with the lowest diameter pins and no pin offset. With this set of results, and a maximum surface temperature design target, the design team would be able to select the design that would have the greatest pump efficiency while achieving the required cooling properties.
“Serverless” Design Studies
This project demonstrated how end-to-end design space exploration can be fully performed by using only cloud-native components. By removing the problems caused by the complexity of setup and maintenance of the required software and hardware stack, full design space exploration can be achieved, even in a ‘serverless’ workflow. Cloud-native components also enable the use of optimization in scenarios and organizations, where previously it was technically and economically not feasible, creating a fully accessible, fully realized design space exploration in new applications.
Learn how connecting Datadvance’s cloud-native low code platform pSeven Enterprise to SimScale’s multiphysics cloud simulation engine using API allows a drastic speedup of simulation and optimization procedures in this on-demand webinar: