The cross flow fan (also called a tangential fan) is used extensively in the HVAC industry, as well as in electronics. It produces an even laminar airflow and allows horizontal or vertical mounting; in addition, a cross flow fan prevents the overheating of components. This type of fan is ideal for limited spaces, due to its long, rectangular form.
Besides its small size, the cross flow fan has further advantages, including high relative efficiency (especially for small pressure and placement), controllable characteristics, very low load when throttled, low speed, and noise. [1]
Optimizing a Cross Flow Fan with CFD Analysis
Early in the design process, fans can be virtually tested with CFD to ensure the highest efficiency and performance and the lowest noise levels are achieved. Simulation software can also help in performing vibration analyses and predicting the aerodynamics of the fan, all of this long before creating a physical prototype.
SimScale’s CFD solution allows fan designers to test different designs in parallel, 100% in the browser, providing flexibility, collaboration options, and access to high computing power—up to 32 cores—from a normal PC or laptop. In this way, designers can make optimization decisions based on the simulation results and deliver the best possible design.
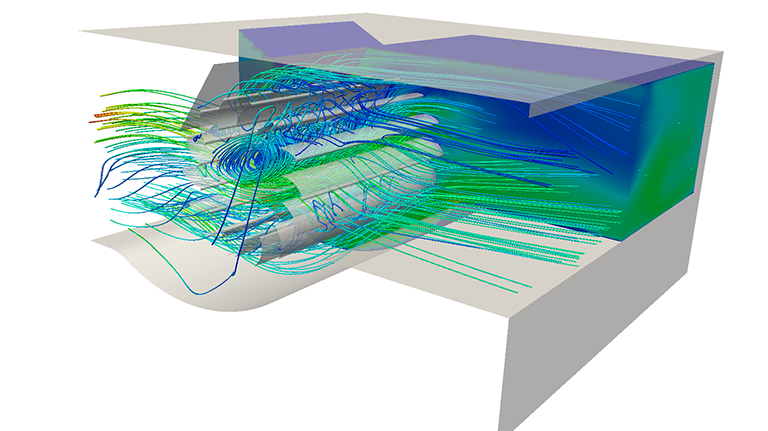
Look at the results of this cross flow fan simulation, which focuses on studying the fan’s aerodynamics and vibration performance.
The design objective was to obtain the maximum flow across the tangential fan while maintaining the lowest possible levels of vibration. Hence it was important for the designer to study and optimize the performance characteristics early in the design stage to avoid substantial costs involved in building physical prototypes.
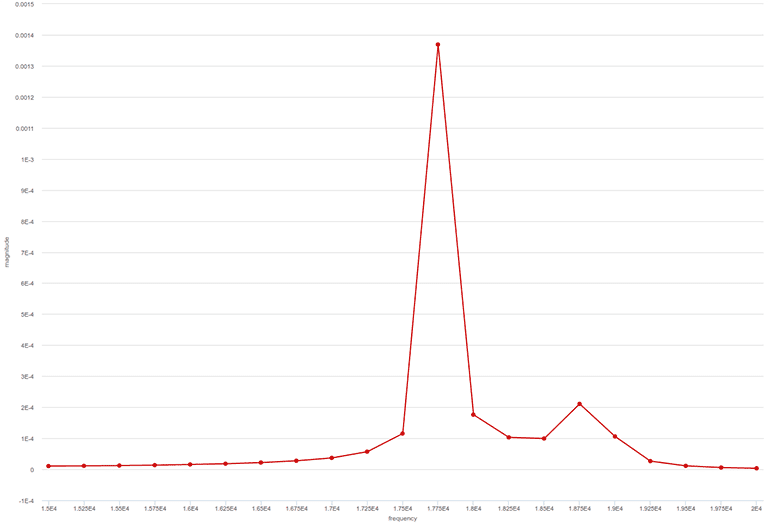
Fan Simulation Results
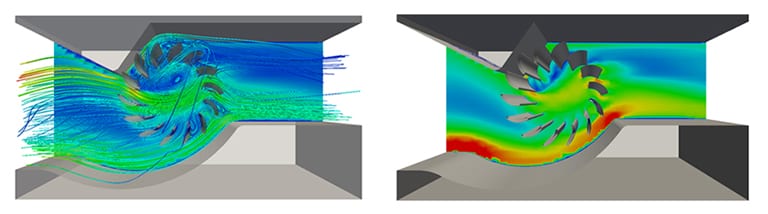
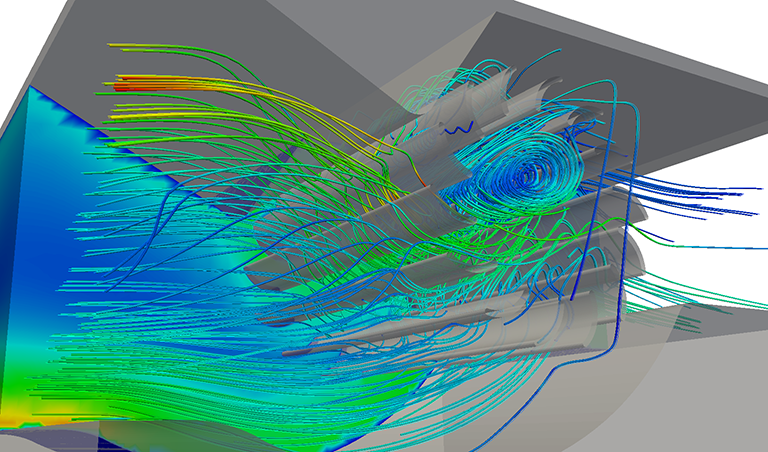
The outcome of this CFD analysis is the visualization of the flow field using contour plots. The engineer’s aim was to predict the maximum airflow for a specific rotation speed of the tangential fan.
The forces which act on the blades were converted to average load, in order to define them as the boundary condition for vibration analysis and reveal the maximum displacements expected due to vibration.
Download our ‘Tips for Architecture, Engineering & Construction (AEC)’ white paper to learn how to optimize your designs!
Download this case study for free to learn how the SimScale CFD platform was used to investigate a ducting system and optimize its performance.
References
- https://www.consortepl.com/crossflow-fans/crossflow-fan-characteristics/