In the midst of the AI boom and endless technological integrations, one technology organizations seem to still treat distinctly is simulation [1]. While both AI and simulation have been at the forefront of technological growth and digitalization, especially in the automotive industry, organizations like OEMs and automotive suppliers have yet to adopt a full integration of AI simulation. This is by no means a lack of technological compatibility; it is merely a case of technological integration in its infancy.
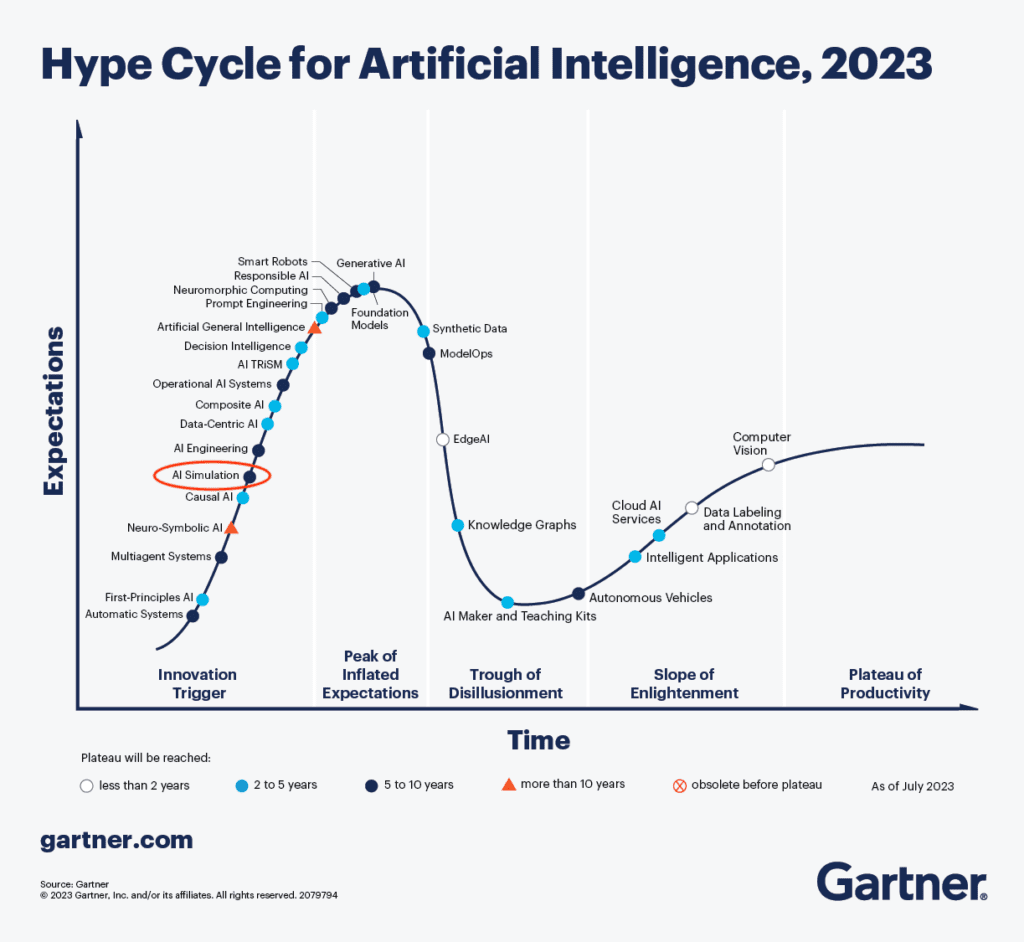
In 2023, researchers at Gartner positioned AI simulation within the so-called “innovation trigger” phase of their famous Gartner Hype CycleTM of AI [2]. This phase is characterized by technology breakthroughs, proof-of-concept stories, and media publicity before it hits the so-called “peak of inflated expectations.” Yet, the pace at which AI simulation has been growing recently has shown significant potential and commercial viability, notably as the engineering simulation space has transformed with the advent of cloud-native simulation.
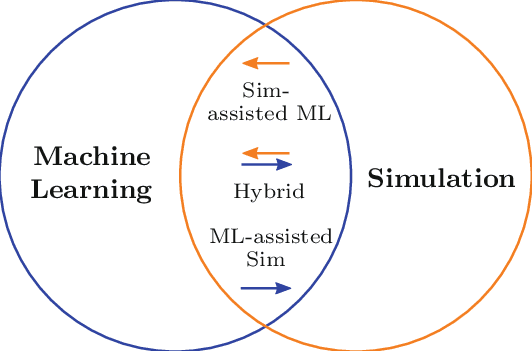
The Convergence of AI and Simulation
Engineering simulation has long been a fundamental tool for refining and validating designs. Throughout the latter half of the 20th century and the early years of the 21st century, simulation software has accumulated extensive data and calculations vital in testing and enhancing various engineering solutions. This has enabled millions of iterations of design optimization, but it has had limitations.
Burdened with hardware, computational, and software limitations, CAE simulation has had convoluted bottlenecks such as the lack of scalability, accuracy-to-speed trade-offs, long simulation cycle times, and, more critically today, long simulation lead times. With the advent of cloud computing, cloud-native simulation has empowered organizations to not only resolve these bottlenecks but also eliminate them altogether.
With cloud-native simulation, scalability is inherent, as engineers and designers can run as many simulations as needed in parallel without being hindered by hardware. As a result, accuracy does not need to be compromised, and simulation lead time is cut from weeks to hours. Furthermore, running simulations online has also allowed organizations to overcome the data siloes between teams, enabling them to collaborate on simulation projects in real time by simply sharing the projects at a click of a button, thus facilitating the company-wide deployment of simulation.
Today, the landscape continues to evolve further with the advent of AI, transforming how we approach simulation. The convergence of AI and simulation is revolutionizing simulation methodologies by infusing them with AI-driven insights and capabilities. The essence of AI simulation lies in its ability to accelerate and enhance the simulation process, making it more efficient, intuitive, and accessible to engineers and designers across the entire design cycle, not merely as a validation step at the end.
At the heart of AI simulation are two pivotal approaches: AI-assisted simulation and simulation-assisted AI.
AI-Assisted Simulation
Here, intelligent AI algorithms are deployed to optimize simulation parameters and processes, streamlining design iterations and accelerating solution convergence. This AI-driven optimization not only expedites the simulation process but also improves its accuracy and effectiveness.
Analysts at Gartner [3] recommend complementing simulation with AI by applying the following:
- Deep learning to accelerate simulation
- Generative AI to augment simulation
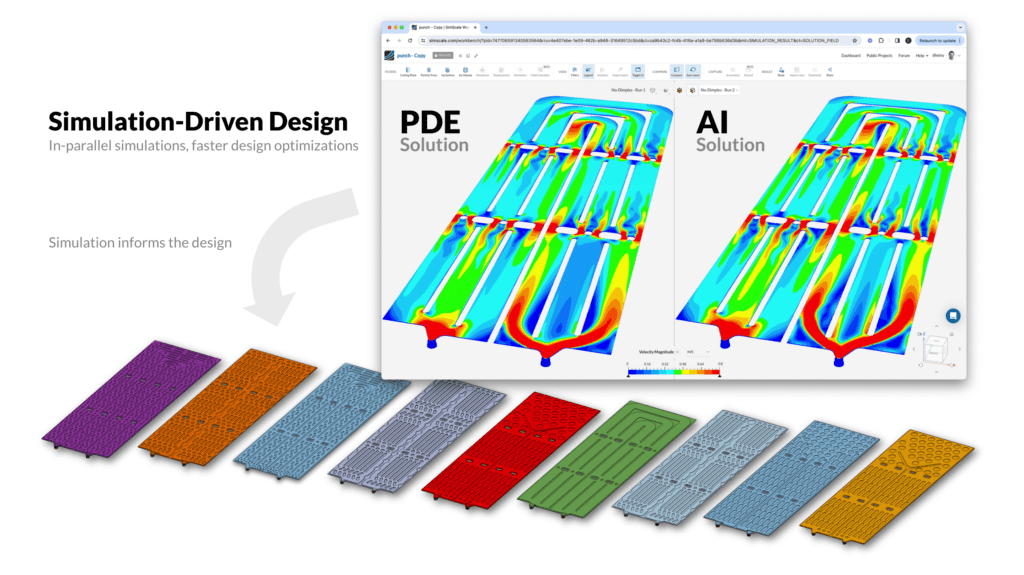
As a result, simulation projects would benefit from AI’s capabilities to increase the speed of executing complex simulations or fill gaps in CAE and simulation models using generative AI. Today, only a cloud-native simulation infrastructure can enable full advantage of AI, as all simulations are immediately ready for AI training on cloud GPUs. As new data is added, retraining of AI models is straightforward. On SimScale’s cloud-native platform, for example, AI CAE Models are deployed next to CFD simulations, with AI results used for near-instantaneous evaluations and CFD for validation.
Simulation-Assisted AI
Simulation-assisted AI leverages simulation outputs to enrich AI models. By integrating insights from simulations, AI models can be trained to understand complex systems better and predict their behavior with greater precision. This symbiotic relationship between simulation and AI empowers engineers and researchers to leverage the strengths of both disciplines, ultimately leading to more robust and insightful engineering solutions.
Supporting AI with simulation data helps optimize business decision-making and overcome the common challenge of real-world data scarcity by providing a data-rich simulated environment for synthetic data generation and reinforcement learning. It is only a matter of time before AI becomes a natural and complementary addition to the use of synthetic data in areas such as automotive, supply chain, electronics manufacturing, and industrial equipment manufacturing.
4 Advantages of AI Simulation
AI simulation offers a multitude of benefits for engineering design, especially regarding process efficiency, accuracy of simulation results, and decision-making. Here are four key advantages that AI simulation provides:
- Accelerated Innovation: One of the most significant benefits is the speed at which AI-enhanced simulations operate. Unlike traditional methods, AI can swiftly analyze vast amounts of data from past simulations and provide results almost instantly. By identifying and examining complex patterns within the data, AI can accelerate the design and optimization process.
- Simulation Democratization: AI-assisted simulations can also help democratize the utilization of simulation technology. Previously reserved for simulation experts, AI simulation can build on top of what cloud-native simulation offers and help make simulation accessible to non-experts. This accessibility fosters collaboration and innovation by enabling a broader range of design engineers to engage in design analysis, allowing for early simulation usage in the design cycle.
- Comprehensive Data: AI simulations integrate multiple models to offer a more comprehensive understanding of complex systems. These simulations provide thorough representations, allowing engineers to gain deeper insights into the behavior of the systems they are designing. This comprehensive approach enhances decision-making and facilitates the creation of more robust and efficient designs.
- Constant Learning: This is an inherent benefit of AI, with its iterative nature promoting continuous improvement. Engineers can refine and enhance their designs with gradually fewer limitations, which leads to more innovative solutions and optimized outcomes, ensuring that designs meet evolving requirements and standards.
Advanced Simulation-Driven Design with AI & Cloud-Native Simulation
The convergence of AI and cloud-native simulation has ushered in a new era of design innovation and efficiency, especially in advancing simulation-driven design. Predictive AI, driven by machine learning models trained on previous relevant data, has the potential to be a game-changer in engineering simulation.
For instance, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) stand out as a particularly powerful method in this domain. They leverage structured node-based data akin to the mesh used in engineering simulations like FEA or CFD. However, the hallmark of GNNs lies in their ability to deliver simulation results within seconds while maintaining reasonable accuracy.
Despite its transformative potential, predictive AI comes with its own set of challenges. The quality of outcomes heavily relies on the quality of input data used for training. For many organizations, data collection and sorting pose significant hurdles in harnessing the full potential of predictive AI models. This is where cloud-native simulation can be the perfect infrastructure for predictive AI.
Through an integrated solution of cloud-native AI CAE, data generation and preparation would be seamless as the data would be 100% compatible and integrated with full traceability. The training of AI models would be constantly implemented on existing GPU infrastructure via high-performance computing (HPC) and would be fully accessible and controllable. All this would enable a flexible and interchangeable use of AI and PDE solvers in a single interface. That is exactly what SimScale is offering today.
In a move reminiscent of OpenAI’s democratization of AI through their LLM-based system ChatGPT, SimScale and NAVASTO have teamed up to make AI-powered simulation predictions accessible to the engineering community. By leveraging cloud-native technologies, they alleviate concerns related to data management, empowering engineers to focus on design innovation without being burdened by the complexities of data handling.
This synergy of AI and cloud-native simulation infrastructure holds immense promise for the future of simulation-driven design spaces. It accelerates the design iteration process and democratizes access to cutting-edge simulation technologies. As more and more organizations embrace this technology convergence, they stand to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, accuracy, and innovation in their design workflows.
References
- Gartner (2023). Innovation Insight: AI Simulation. https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/4037399
- Gartner (2023). What’s New in Artificial Intelligence from the 2023 Gartner Hype Cycle. https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/what-s-new-in-artificial-intelligence-from-the-2023-gartner-hype-cycle
- Cosmotech (2023). Gartner Highlights Powerful Combination Of AI & Simulation. https://cosmotech.com/resources/article/gartner-highlights-powerful-combination-of-ai-simulation/
- von Reuden, L. et al. (2020). Combining Machine Learning and Simulation to a Hybrid Modelling Approach: Current and Future Directions. International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis (IDA). 548-560. DOI:10.1007/978-3-030-44584-3_43