With a host of different simulation software options available on the market today, if you are in the process of choosing your future CAE software package for engineering consulting services, there are many aspects to consider. Computational power, price, ease of use, and that’s before you get to the different simulation types available. It can be a complicated procedure. However, to de-mystify the process, in this article, we will cover the essential aspects to consider, along with identifying the main advantages and disadvantages of three distinct types of simulation software: on-premises, open source and cloud-based. Remember, CAE software has the potential to become one of the most important engineering tools in your arsenal, and this decision could have long-term consequences, so taking the time to learn about your options is worthwhile.
What Do You Need to Consider when Selecting CAE Software?
Purpose and Physics
The natural place to begin when deciding on a CAE software solution is the physical process you want to simulate for your product or building, and the environment it operates in. Are you interested in investigating fluid dynamics (CFD)? Static stress on an object (FEA)? Or are you interested in more advanced modeling, such as conjugate heat transfer or FSI (fluid-structure interaction)? Not every software package is equal in this regard, and it’s important to make sure that the software you choose is able to specialize in your particular area of interest.
Pricing and Licensing Policy
A variety of pricing models exist for CAE software, ranging from free open source solutions, through to pay-as-you-need models or commercial floating licenses. To plan ahead with your budget, it’s important to look both at the expected frequency of your simulations, and the number of users that will be required at any one time. Is there a way to avoid a bottleneck in resources?
Hardware Requirements
Engineering simulation (CAE) can be computationally demanding and therefore expensive, especially for smaller companies. If you plan to run high-resolution, transient analyses, it’s important to invest in the right computer equipment. When it comes to users, does it make sense to invest in a cluster? Or are there other resources available?
Additional Software Requirements of Engineering Consulting Firms
CAE (computer-aided engineering) is an umbrella term that includes various software and analysis types, such as CAD (computer-aided design) and the aforementioned CFD and FEM simulation techniques. In terms of a project workflow, it’s unlikely you’ll be dealing with a single solution. To this end, it’s vital that your data is convertible between programs. In terms of simulation, an important aspect to consider is whether or not the package you are contemplating contains tools to prepare your geometry for simulation. Can it mesh your domain, or do you need to buy separate meshing software?

Moreover, how do you post-process your results? The size of these results can reach several gigabytes, do you have a plan to handle this data both in terms of hardware and your Internet/network connection?
Ease of Use
When selecting CAE software for your engineering consulting firm, it has to be productive; in this case, that means the software must be:
- easy to learn
- easy to use
- fast
It might also be beneficial if the installation and licensing process is as simple as possible. When it comes to cloud computing, no installation is necessary. This increases both ease of use and flexibility, the software is available on any computer, anytime.
Accessibility
Another aspect that could influence your decision is the accessibility of your software and hardware. For example, if you are frequently traveling, how can you access your simulations? Is it possible to take your results with you to a meeting, or do you need to create a presentation every time? If so, does the software package contain an automatic reporting tool?
Data Management
In engineering consulting, each project has the potential to generate massive amounts of data. These files take time to download and post-process. How efficient is the software I/O module? How efficient is the post-processing software? Is it able to handle larger files?
On-Premises CAE Software Packages (Desktop Applications)
Under the term “on-premises software” in the CAE industry, we generally mean programs that are installed on local workstations and/or on the in-house cluster of the engineering consulting firm. There is, usually, a floating licensing module that distributes the purchased license credits to the active users, introducing a maximum limit of parallel jobs, thus creating a bottleneck at peak times. ANSYS, Comsol, EXA, StarCCM+ are the biggest players in this category, just to name a few. While user-friendliness and simulation workflow are well optimized, this usually comes at a price; costs for commercial CAE package can range from $10,000 to $50,000+ per workstation. Extending your simulation capabilities to utilize a larger amount of cores will further increase the budget required, making the turnaround time more expensive.
Learn how to use fluid flow simulation to test and optimize ventilation of hospitals and other healthcare environments.
Open Source CAE Software
An open source software, by definition, does not necessarily mean “license-free” or “free”. It simply means that the code of the program is openly accessible to the public; therefore, anybody can read and modify it. That being said, there are certainly open source CAE software packages that are free for individuals and companies to use, such as OpenFOAM, Elmer, and SU2. For each of these programs, no upfront payment is required in order to download and use them. They are, however, licensed under the Creative Commons policy. In practice, this means that if you modify the code and release it, it has to remain open source and free.
While there are obvious benefits that come from using an open source CAE software (price, flexibility, etc.), they are significantly less user-friendly straight out of the box. For a beginner CAE engineer, as well as for infrequent users, they can be frustrating and inconsistent to use.
Bringing It All Together: CAE Software in the Cloud, Integrating Open Source Solvers
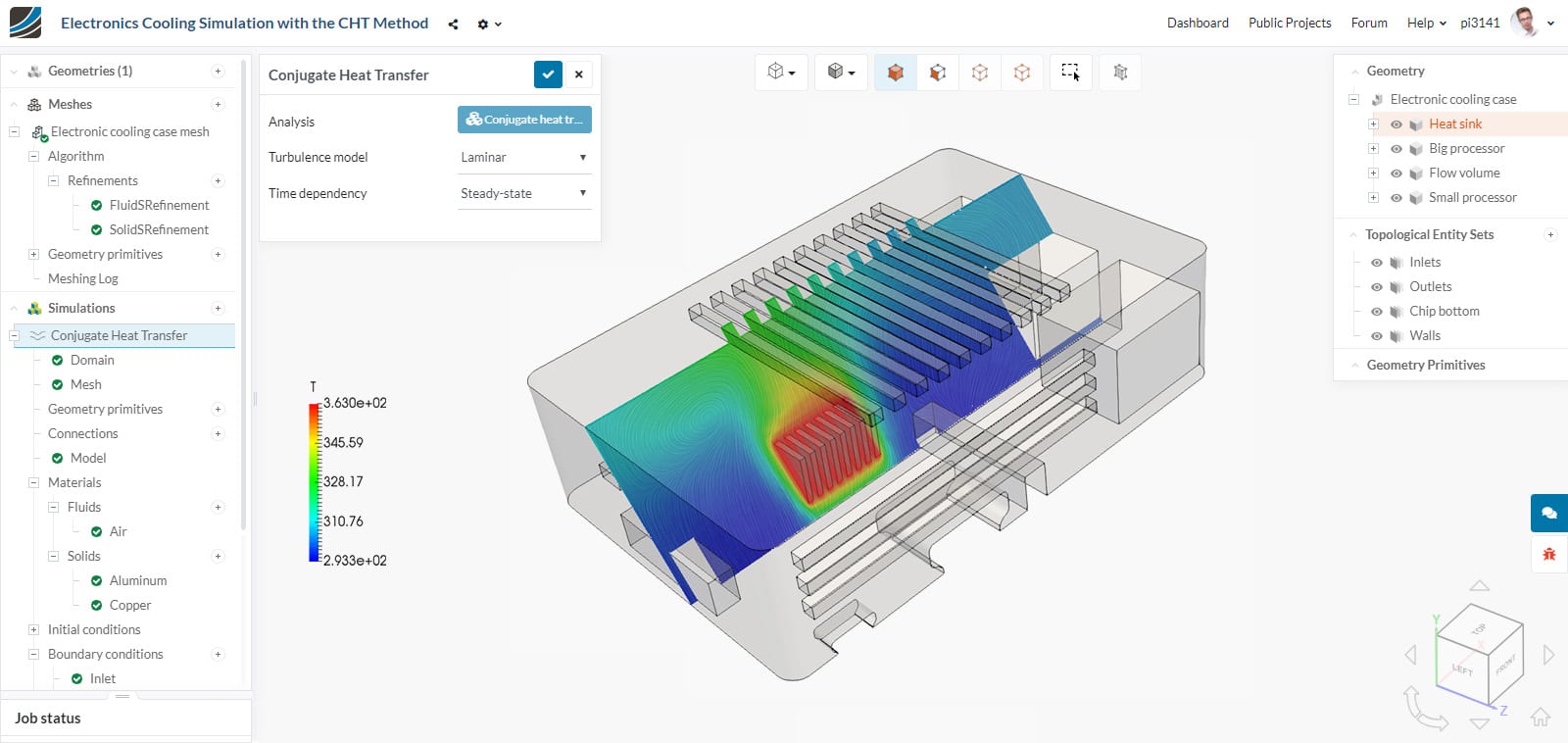
SimScale is a distinct concept that combines the benefits of open source technology with cloud access, license flexibility, hardware efficiency, and accessibility. The SimScale platform is a powerful, advanced CAE tool that has the same speed as the most expensive on-premises packages, with the added benefit of user-friendliness, enhanced through the recent release of Workbench 2.0.
With SimScale, there is no physical limitation on licenses. You can run as many simultaneous simulations as you need thanks to the elastic cloud feature. In addition, customers can scale their simulation power as needed, having the possibility to use machines of up to 96 cores.
Accessibility is world-class; with just a normal computer and Internet connection, you can work from anywhere, take your results with you, and easily present your project at any meeting, anywhere. You can download the results of your simulations anytime, allowing you to present, refine or post-process further on your local hardware.
Furthermore, our flexible pricing model scales to fit your needs. Depending on whether you are a small engineering consulting firm or a product company with several CAE engineers, our team works with you to find the best offer to fit your budget with SimScale.



